· Two series of 22 and 15 atom cyclic enkephalins incorporating a diversely substituted guanidine bridge have been prepared to assess the potential effect of the bridge substitutions on their opioid activity profile The most notable results were obtained with the shortest cyclic analogues, which showed a significant variation of their binding affinity toward μ and δ opioidUsing a structure estimation method based on molecular connectivity indices(1), the Koc of guanidine can be estimated to be (SRC) According to a classification scheme(2), this estimated Koc value suggests that guanidine is expected to have very high mobility in soil(SRC) The pKa of guanidine is 125(3), indicating that this compound will exist almost entirely as a cation in the environment(SRC) As a result, guanidineView Entire Discussion (0 Comments) More posts from the OrganicChemistry community 161 Posted by 2 days ago Cyclopentanone
A Which N Of Guanidine I Is More Basic And Is More Likely
Guanidine minor resonance structure
Guanidine minor resonance structure-A comparative study on the aggregating effects of guanidine thiocyanate, guanidine hydrochloride and urea on antagonist (IL1ra) are strongly denaturantdependent as evidenced by highresolution twodimensional nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), limited proteolysis, and smallangle Xray scattering (SAXS) The folded ensemble was characterized in detail in the presenceLa guanidine est un composé cristallin formé lors de l'oxydation de la guanineElle est utilisée dans la production de plastiques et d'explosifs Elle se trouve également dans l'urine, étant un produit du métabolisme Elle n'est pas commercialisée telle quelle, mais sous forme de sel (chlorhydrate, acétate, carbonate, etc)Elle peut également céder un proton
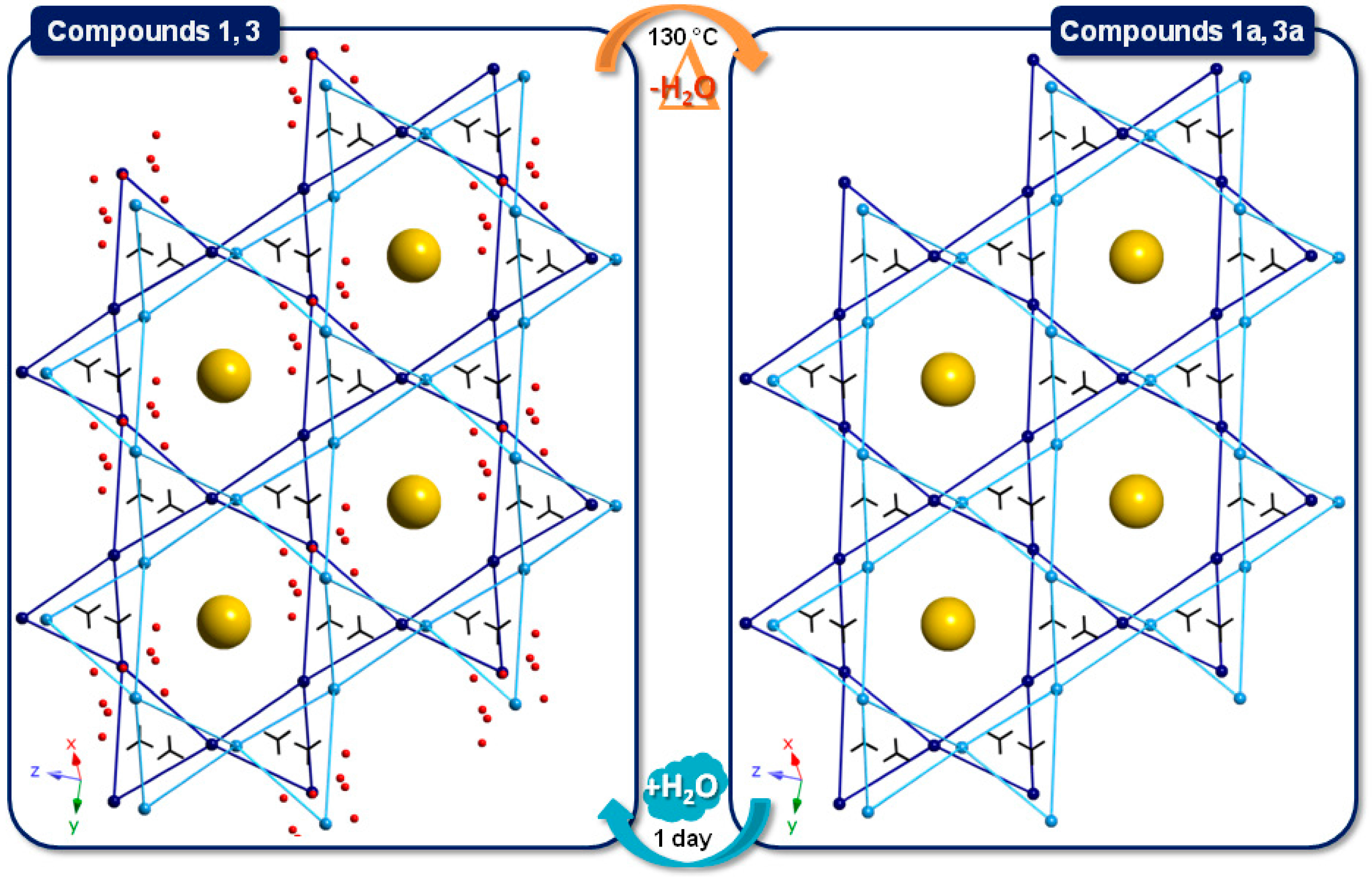


Inorganics Free Full Text Single Crystal To Single Crystal Reversible Transformations Induced By Thermal Dehydration In Keggin Type Polyoxometalates Decorated With Copper Ii Picolinate Complexes The Structure Directing Role Of Guanidinium Html
Pharmacology Accelerate your drug discovery research with the industry's only fullyAll Organic Chemistry Practice Problems Major and Minor Resonance Contributors Practice ProblemsWhich one is it?
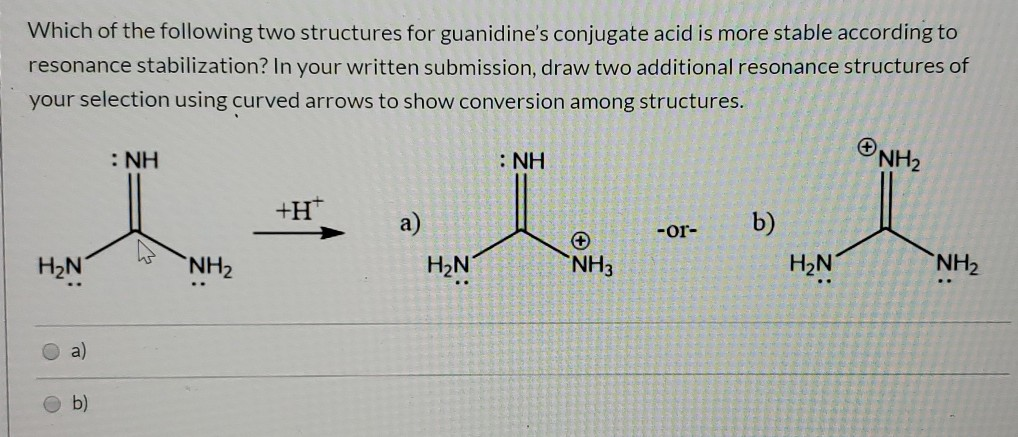
The electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spin labeling technique has been employed to study the properties and conformation of the thiol protease papain in solution, using (1oxyl2,2,5,5tetramethyldelta 3pyrroline3methyl) methanethiosulfonate (MTS) as the spin label The measurements of papain's amidase activity corroborate the EPR results The major findings areChemistry Organic Chemistry Following is a structural formula for guanidine, the compound by which migratory birds excrete excess metabolic nitrogen The hydrochloride salt of this compound is a white crystalline powder, freely soluble in water and ethanol (a) Write a Lewis structure for guanidine showing all valence electronsOf two possible structures A and B for the conjugate acid of guanidine, the more stable is the one that is better stabilized by electron delocalization Which one is it?
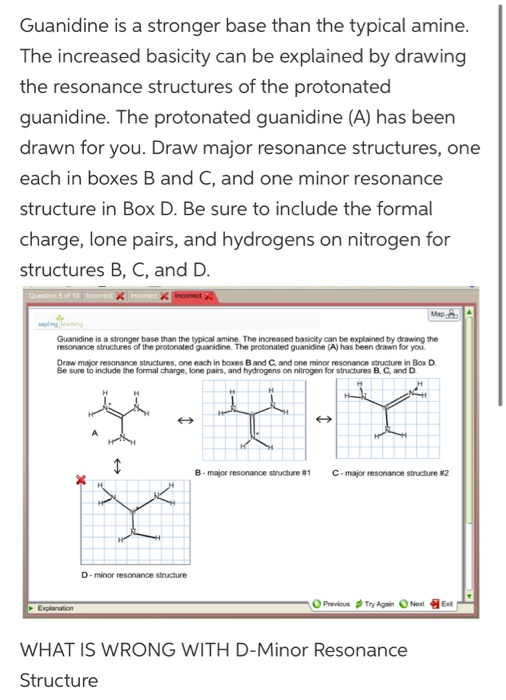
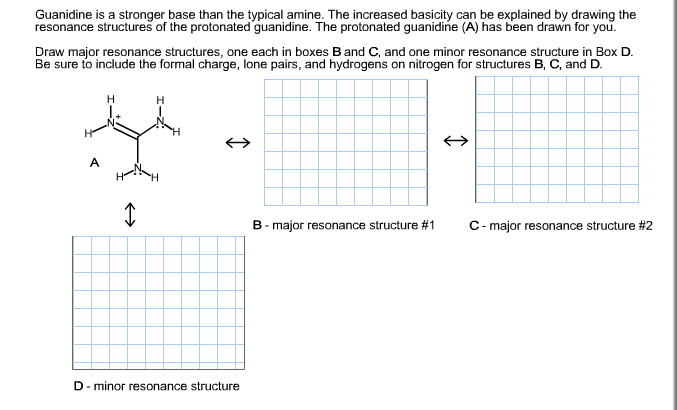
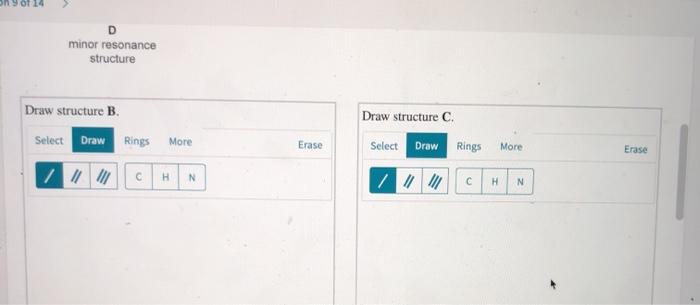
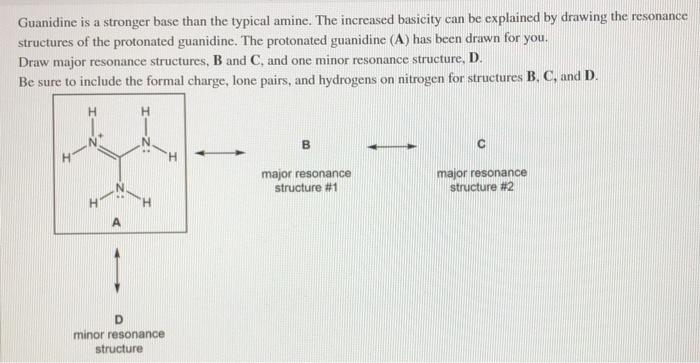
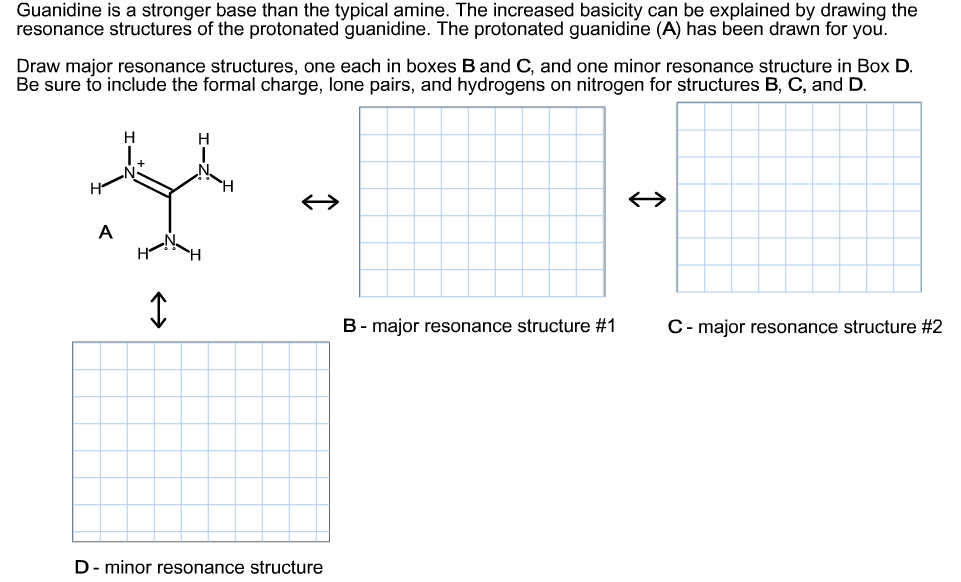
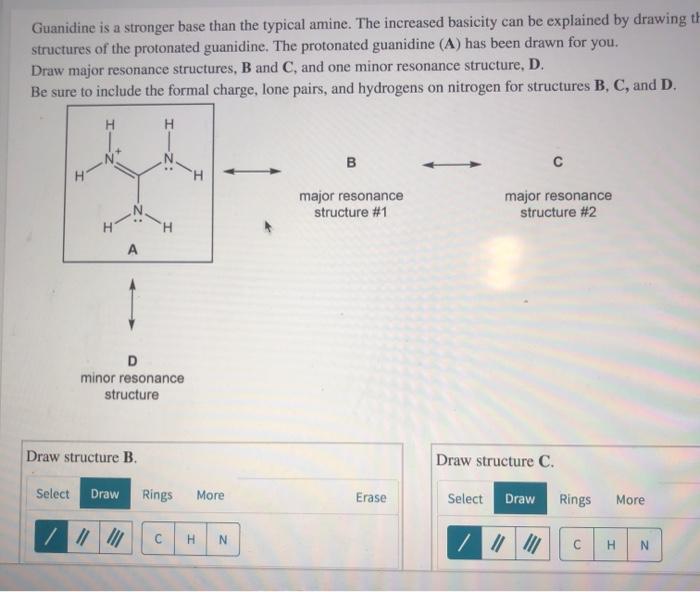
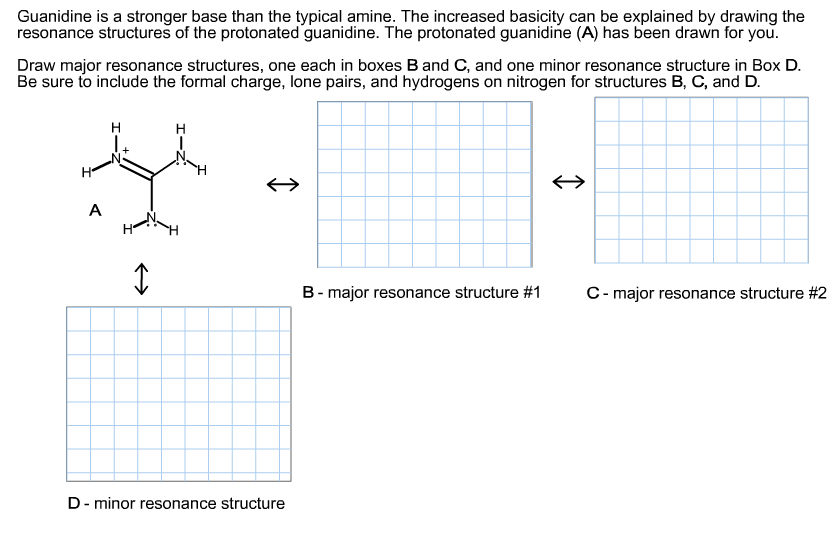
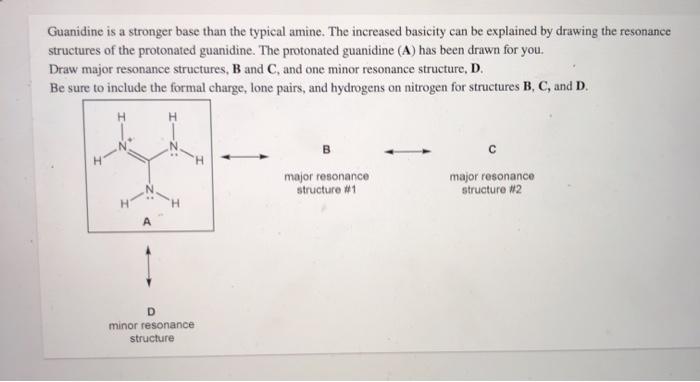
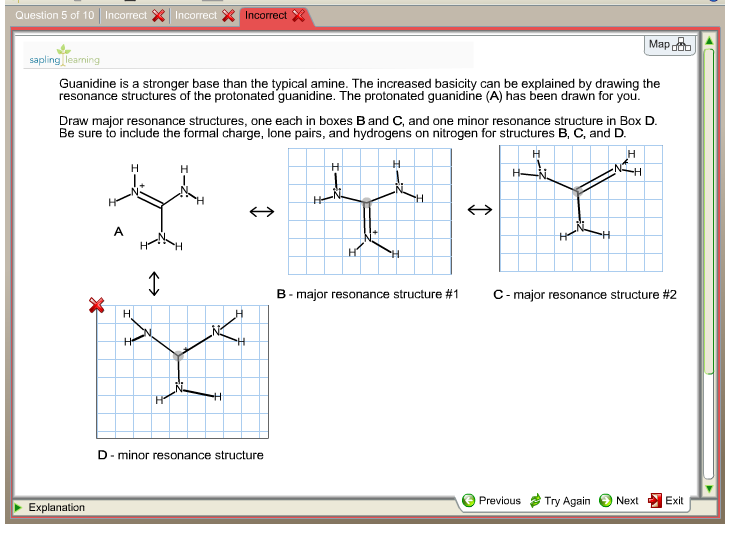
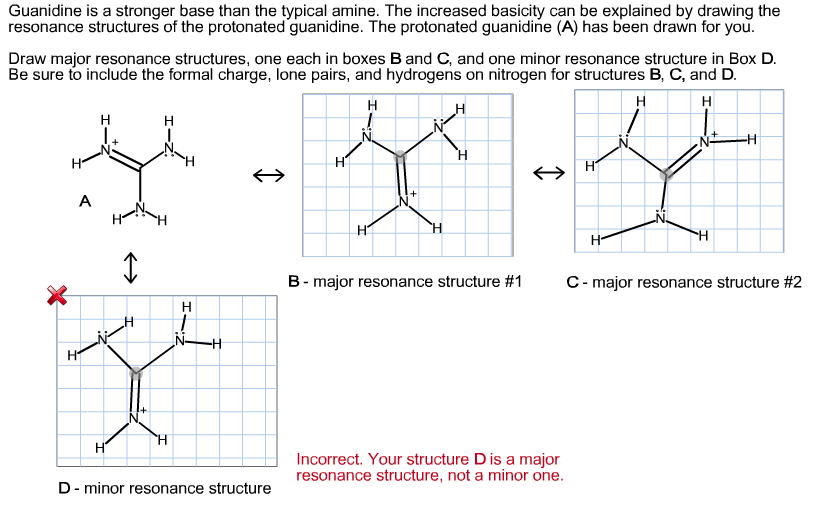
Guanidine is a stronger base than the typical amine The increased basicity can be explained by drawing the resonance structures of the protonated guanidine The protonated guanidine (A) has been drawn for you Draw major resonance structures, one each in boxes B and C, and one minor resonance structure in Box D Be sure to include the formal charge, lone pairs, and hydrogens · Structures that don't obey the octet rule are usually** minor resonance structures *in an absolute value sense ** there are some exceptions, like BF3 where the boron has only 6 electrons in the major resonance structure 4 0 Juanita Lv 4 5 years ago For the best answers, search on this site https//shorturlim/awkHQ Resonance structures usually have to have aOne contributing resonance structure to a resonance hybrid is given Curved arrows are used to show how electron pairs move to generate a second resonance strucutre Which statement is true?



Out Of The Given Compounds A And B The Number Of N Atoms In The Compound Which Is More Basic Are



Synthesis And Characterization Of A New Energy Material Guanidinium Dinitramide With Crystallization Solvent Sciencedirect
Arginine has a guanidine structure in the protonated form as guanidinium ion, which functions as an efficient identification moiety of anionic substrates suc h as carboxylate, nitronate, andStructure, properties, spectra, suppliers and links for Guanidine,Both the guanidine and guanidinium type stabilizations have been characterized in terms of a number of structural and energetic parameters degree of single/double bond character from bond lengths and π‐bond orders, electron distributions, and protonation energies The major finding is that the structural and energetic properties of the isolated extended‐guanidinium group
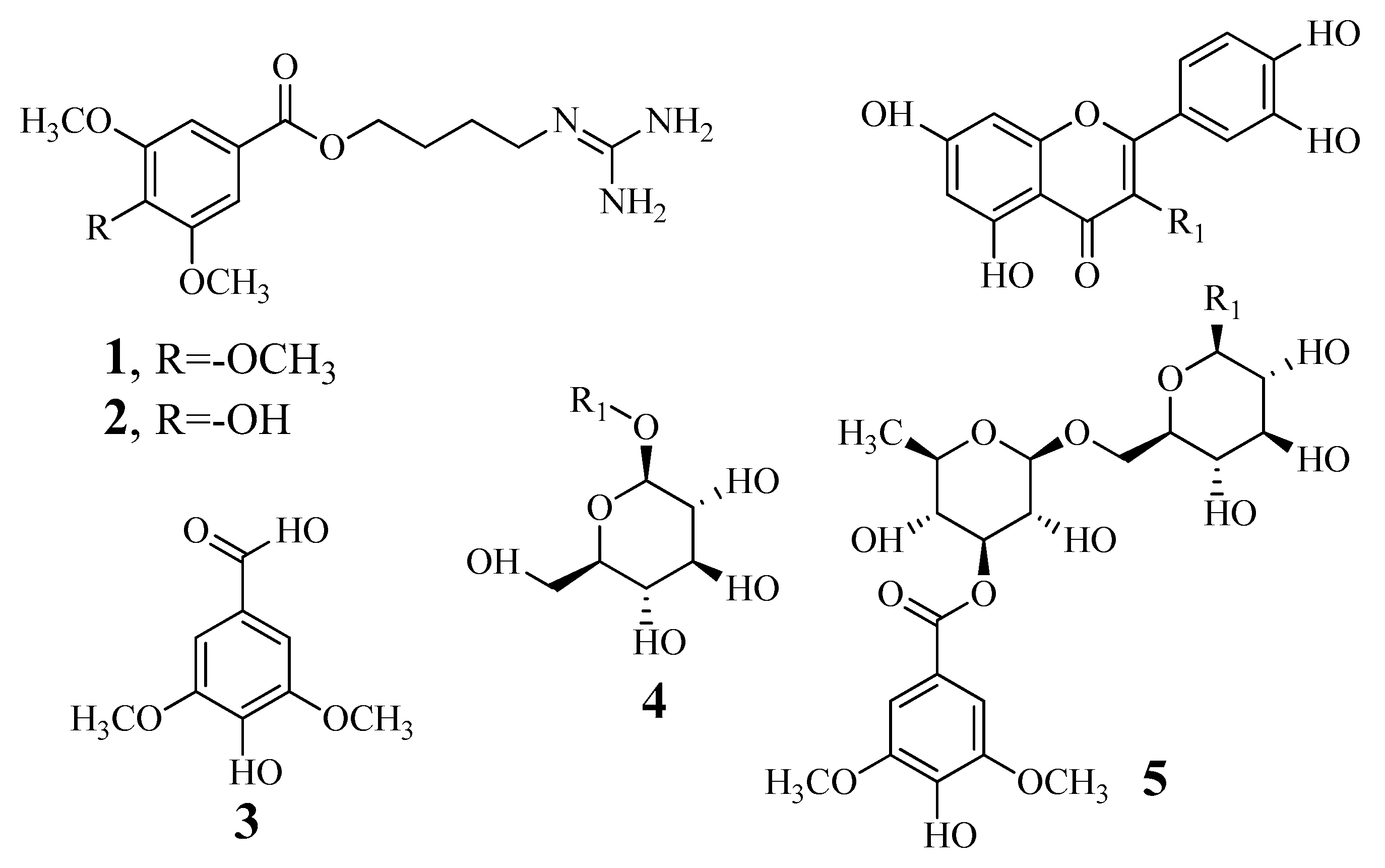


Biomolecules Free Full Text The Guanidine Pseudoalkaloids 10 Methoxy Leonurine And Leonurine Act As Competitive Inhibitors Of Tyrosinase Html



Antimicrobial Drugs Bearing Guanidine Moieties A Review Sciencedirect
Guanidine is a general protein denaturant, unfolding proteins and altering their threedimensional structure Consequently, some proteins will be irreversibly altered upon interaction with guanidine solutions and may lose their binding function Before any largescale use of guanidine, it is best to test a small sample and determine whether the denaturing effects will adversely affect theLet's look at a few the patterns for drawing resonance structures and the first pattern we're going to look at is a lone pair of electrons next to a PI bond and so here's a lone pair of electrons I'm going to highlight it in magenta that lone pair of electrons is located on this carbon let me go and put this carbon in green here and I'm saying there's a and there's a negative 1 formal charge · Resonance structures of guanidine I have learned about the octet rule, and I saw in some examples that it is however possible for a Catom to only have 6 electrons around him (like in pyridin ) So when i tried to calculate the Resonace structures of guanidine, I wondered why there must be 8 electrons around C this time (like this video )


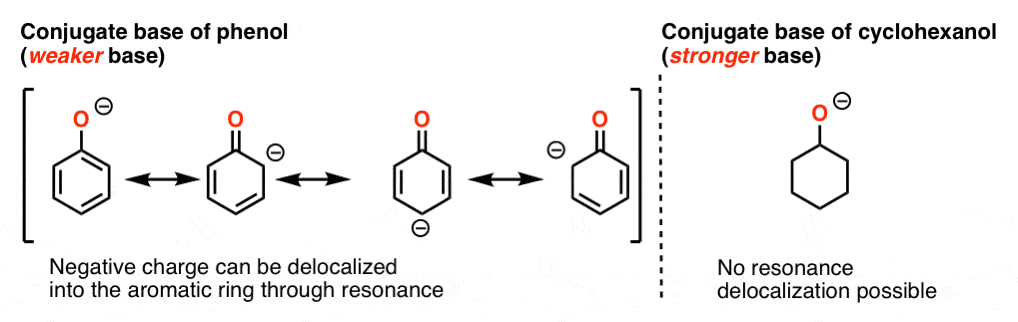
5 Key Basicity Trends Of Amines Master Organic Chemistry


Solved What Are The Resonance Structures And Which Is The Chegg Com
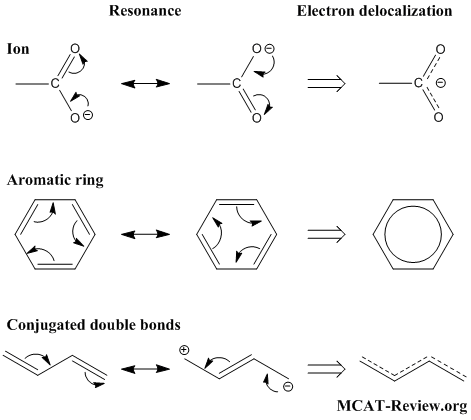
Major and Minor Resonance Structures September 17, 15 By Leah4sci Leave a Comment Once you've mastered the rules for which electrons to resonate (video 2) it's important to understand which resonance structures are considered important or major contributors, and which are considered less important or minor contributorsGuanidine studies on the reaction with ethyl N(2amino1,2dicyanovinyl) Structure 14 is tentatively assigned to this new product Keywords Guanidine, pyrimidine, imidazole, triazepine, cyclization Introduction Guanidine, a nitrogen organic base, has been widely used in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds incorporating at least two nitrogen atoms This moiety is present inFigure 2 Chemical structure of guanidine Important of Guanidine group As we mentioned that guanidinium moiety is found in Arginine amino acid, this amino acid is fou nd in


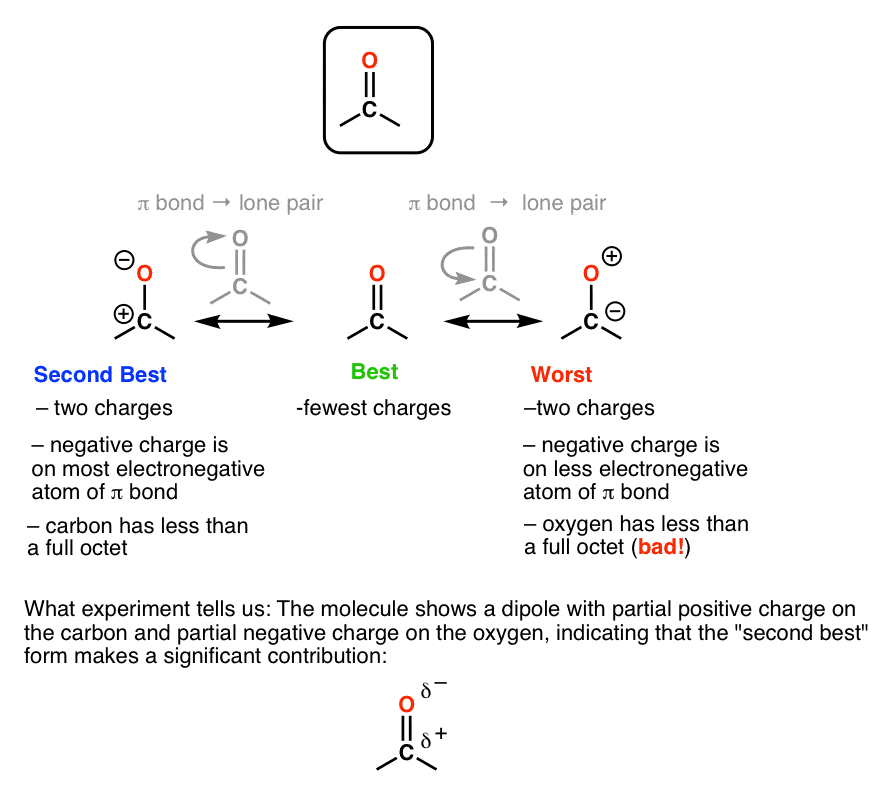
How To Find The Best Resonance Structure By Applying Electronegativity



Resonance Structures Of Nucleobases 5 A 6 B And 7 C In Download Scientific Diagram
There are no $\mathbf{sp^3}$ nitrogens in guanidine Guanidine is isolobal to urea, where the carbonyl oxygen has been replaced by an imine $\ce{NH}$ However, in principle it is still the same flat, resonancestabilised molecule The main difference is that there is no 'preferred' site for the double bond — it could point towards any of the three nitrogens in theory;A very minor contributor, like V, adds very little to the picture and are normally ignored Rank by energy Each contributor corresponds to a unique electron pattern, or wave function, for the molecule The lowest energy wave functions will always be major contributors Higher energy wave functions will be minor contributors, and their importance will diminish as their energy rises HighBoth the guanidine and guanidinium type stabilizations have been characterized in terms of a number of structural and energetic parameters degree of single/double bond character from bond lengths and π‐bond orders, electron distributions, and protonation energies



Guanidine An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Inorganics Free Full Text Single Crystal To Single Crystal Reversible Transformations Induced By Thermal Dehydration In Keggin Type Polyoxometalates Decorated With Copper Ii Picolinate Complexes The Structure Directing Role Of Guanidinium Html
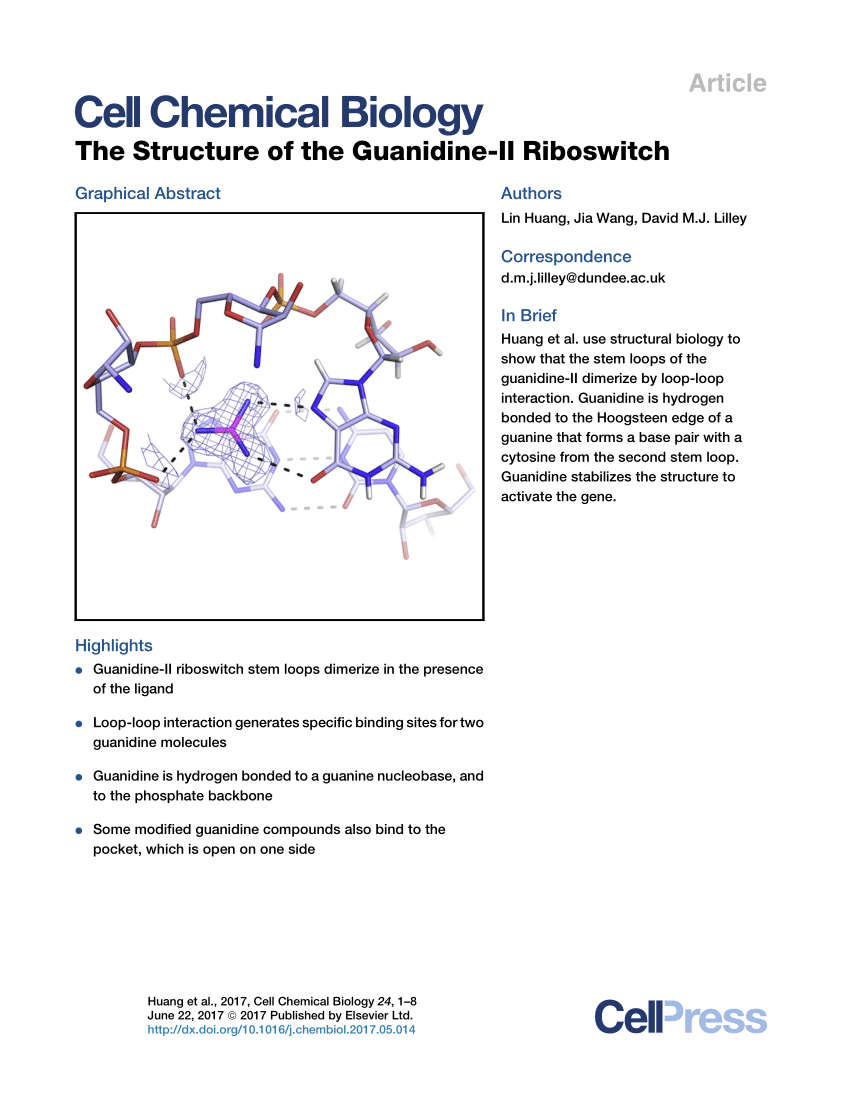
· The structure of the guanidineI riboswitch is dominated by a long continuous set of coaxially stacked helices that includes P1, P1a, P1b, and P2 The large internal loop between P1 and P1b forms a helix, P1a, that extends this helical stack An additional helix, P3, forms between conserved nucleotides in the extended tail at the 3′ end of the sequence Helices P1a and P3Search results for guanidine at SigmaAldrich Compare Products Select up to 4 products *Please select more than one item to compareClick here👆to get an answer to your question ️ In the following sets of resonating structure, label the major and minor contributors towards resonating hybrid



Antimicrobial Drugs Bearing Guanidine Moieties A Review Sciencedirect
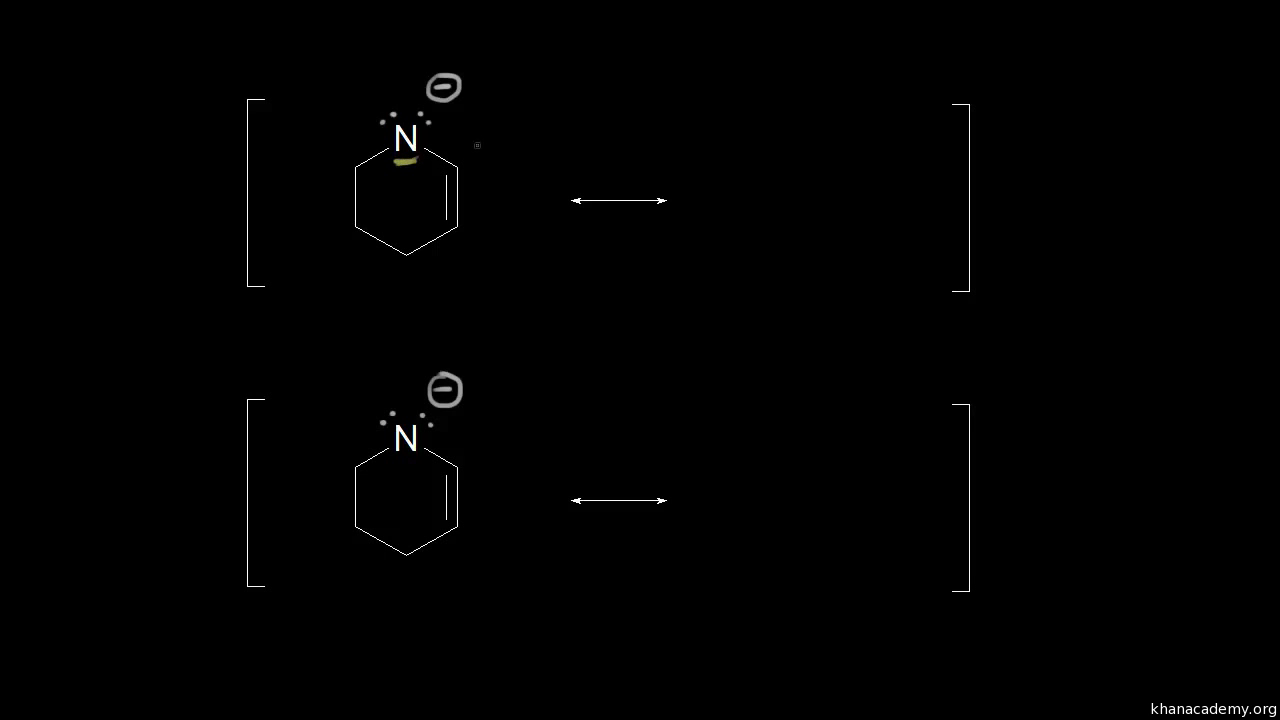


Common Mistakes When Drawing Resonance Structures Video Khan Academy
Resonance hybrids are really a single, unchanging structure Major resonance contributors of the formate ion Representations of the formate resonance hybrid 2) The resonance hybrid is more stable than any individual resonance structures Often, resonance structures represent the movement of a charge between two or more atoms The charge is spread out amongst theseThe O2 reduction reaction (ORR) catalysed by iron porphyrins with covalently attached pendant guanidine groups is reported The results show a clear enhancement in the rate and selectivity for the 4e−/4H ORR In situ resonance Raman investigations show that the rate determining step (rds) is O2 binding to f 19 Chemical Science HOT Article CollectionTo draw resident structure for this molecule and then to label, which is the major contributor of the minor contributor and to draw the residents hybrid So the first thing we're asked to do is draw resident structure for this Um, this is fairly straightforward So we have a double bond bond We have lone pairs adjacent to it, so we can just move alone pair and the double bond So one of the



How To Predict The Basicity Of Organic Amines Chemistry Stack Exchange


Major And Minor Resonance Structures Organic Chemistry Socratic
· Molecular structure of guanidine polymer was characterized by 2D NMR spectra (C–H COSY) Dynamic antimicrobial process was investigated by measuring the UV 260 absorbance of bacterial suspension with various guanidine polymer concentrations according to the contact time Morphology of bacterial cells exposed to guanidine polymer was also visualized using AFMChemical Entities of Biological Interest (ChEBI) is a freely available dictionary of molecular entities focused on 'small' chemical compoundsMolecular structures of relevant crystals were obtained through single crystal Xray diffraction These structures revealed a complex hydrogenbonding network within these ionic species, and showed efficient delocalization of the formal positive charge within the protonated guanidinium units The guanidine superbases were implemented in a series of reactions attempting the



Protonation Of Guanidine Chemistry Stack Exchange



The Predicted Stabilities Of Resonance Contributors Mcc Organic Chemistry
A major motivation of our study was to compare cellular turnon kinetics for a riboswitchbased biosensor versus reporter for the same ligand, which to our knowledge has not been done To construct the Kpn guanidine reporters, the synthetic promoter BBa_J and the 5′ untranslated region of the K pneumoniae tauA gene containing the guanidine riboswitch (with or without M4You could say the diamide · guanidine – guanidine – guanidine With a central carbon surrounded by three nitrogens, a guanidine group allows this transform in three possible orientations amide – imidic acid H−N−C=O ⇌ N=C−O−H (eg, the latter is encountered during nitrile hydrolysis reactions)



Organic Chemistry Video 17 Resonance Example 13 Guanidine Youtube


Major And Minor Resonance Structures Organic Chemistry Socratic
Guanidinium is a guanidinium ion It is a conjugate acid of a guanidine and a carbamimidoylazanium A strong organic base existing primarily as guanidium ions at physiological pH It is found in the urine as a normal product of protein metabolism It is also used inThis free chemistry help video tutorial shows you how to create and understand resonance structures for the acetate ionBy convention, resonance contributors are linked by a doubleheaded arrow, and are sometimes enclosed by brackets In order to make it easier to visualize the difference between two resonance contributors, small, curved arrows are often used Each of these arrows depicts the 'movement' of two pi electrons



The Crystal Structure Of H 2db Complexed With A Partial Peptide Epitope Suggests A Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Assembly Intermediate Journal Of Biological Chemistry



Resonance Structures Of Nucleobases 5 A 6 B And 7 C In Download Scientific Diagram
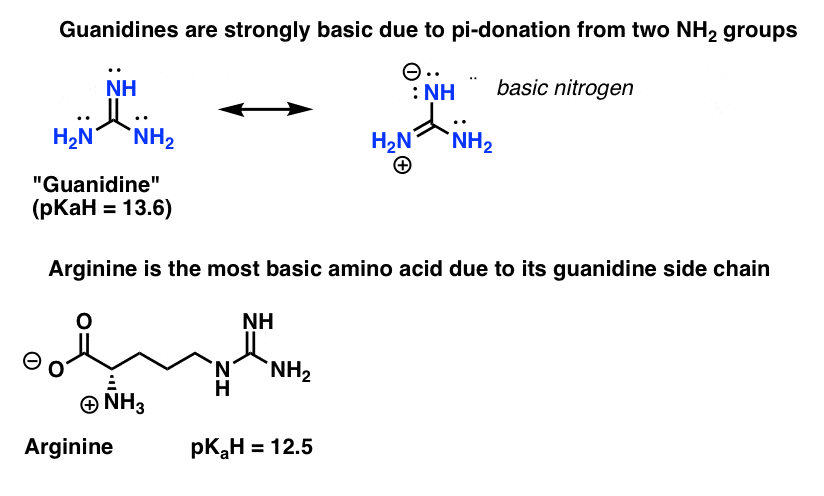
The alkyl chain structure significantly affects the binding constant and energy change value of the polymermembrane interactions and the perturbation extent of the phospholipids membrane, which lead to the different biocidal activity of the polymer analogs This work provides important information about the membrane disruption action mechanism of biocidal guanidineStructure Guanidine can be thought of as a nitrogenous analogue of carbonic acid It is a highly stable 1 cation in aqueous solution due to the efficient resonance stabilization of the charge and efficient solvation by water molecules As a result, its pK a is 136 8 meaning that guanidine is a very strong base in water;Explain pls 0 comments share save hide report 100% Upvoted Log in or sign up to leave a comment Log In Sign Up Sort by best no comments yet Be the first to share what you think!



Resonance Structures Of Nucleobases 1 A 2 B 3 C And 4 D In Download Scientific Diagram



Resonance Structures Of Nucleobases 5 A 6 B And 7 C In Download Scientific Diagram
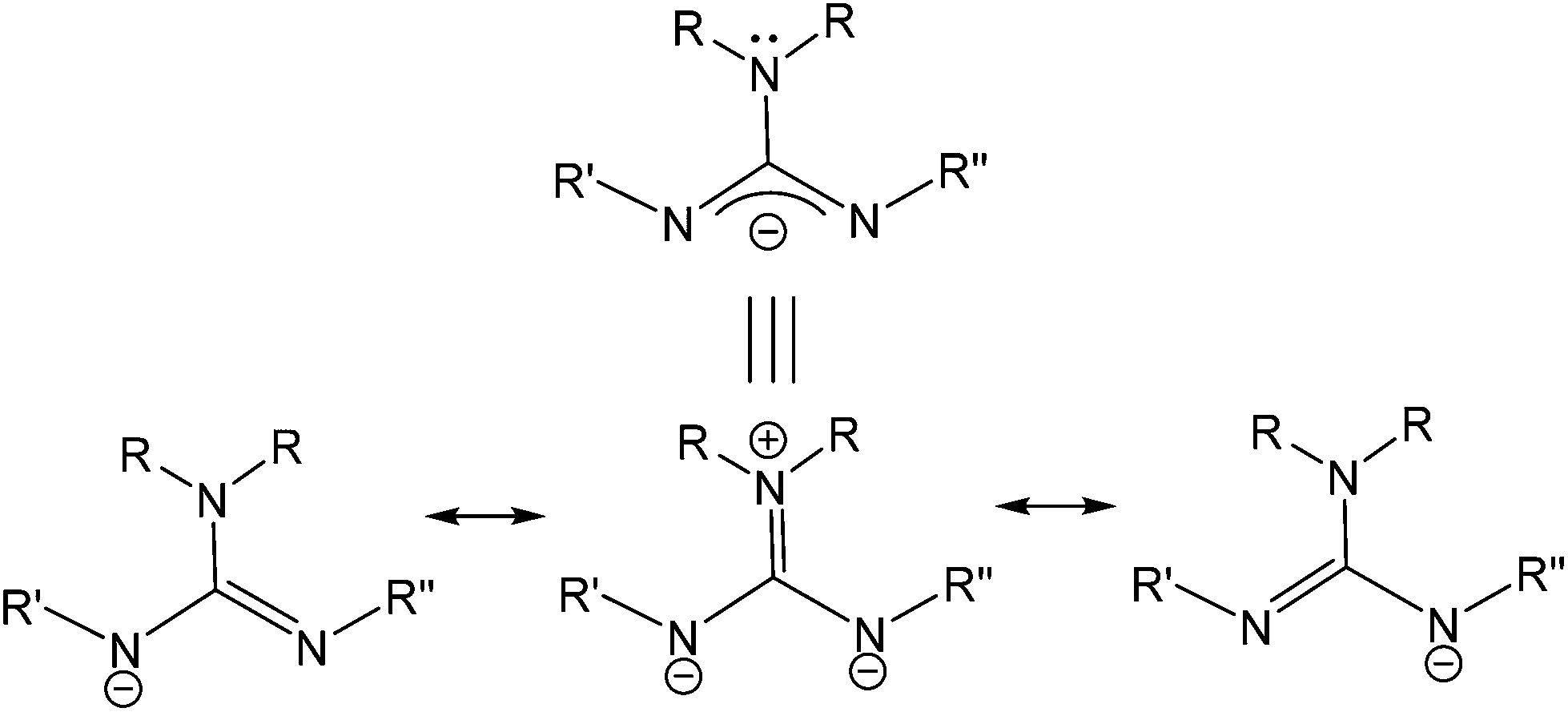
E 2 pts Guanidine is an exceptionally strong amine base Explain, providing the resonance structures of the conjugate acid q The conjugate acid of guanidine has 3 equivalent resonance structures, along with one other canonical structure, and is therefore rather highly resonance stabilized This makes it very easy to protonateMinor resonance structures are all the resonance contributors that are higher in energy than the lowestenergy contributor For example, we can draw three possible contributors for formamide, HCONH₂ We have to decide which of these is the lowestenergy form That one will be the major contributor All the others will be minor contributorsStructure 3D Download MOL SDF 3DSDF PDB SMILES InChI Similar Structures Structure for Guanidine (DB) × Close Weight Average Monoisotopic Chemical Formula CH 5 N 3 Synonyms Aminomethanamidine;



One Contributing Resonance Structure To A Resonance H


An Efficient Synthesis Of Indolo 2 3 B Quinoline Guanidine Derivatives With Their In Vitro And In Vivo Study Springerlink
In neutral water, it exists almost exclusively as guanidiniumAn unusual type of π‐electron delocalization in Y‐shaped molecules related to guanidine and its protonated form, the guanidinium ion, has been studiedAre all the resonance structures of guanidine major contributors?
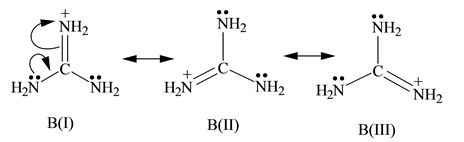


Solved Of Two Possible Structures A And B For The Conjugate Acid Chegg Com



A Which N Of Guanidine I Is More Basic And Is More Likely
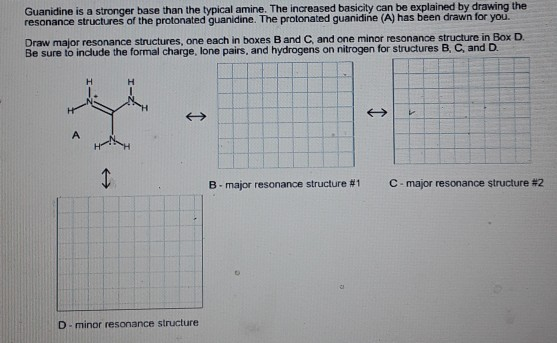
A Structure X and the given structure are of equal importance B Structure X is less important than the given structureMolecular structure of guanidine–type surfactants and their aggregation properties12,13) Dodecylguanidine hydrochloride (C 12A 0G) easily forms micelles because hydrogen–bonding between the guanidine groups facilitates the self–assembly of the surfactant molecules in aqueous media The spacer group between guanidine group and alkyl group of LAG was found to weakenGuanidine is a stronger base than the typical amine The increased basicity can be explained by drawing the resonance structures of the protonated guanidine The protonated guanidine (A) has been drawn for you Draw major resonance structures, one each in boxes B and C, and one minor resonance structure in Box D Be sure to include the formal charge, lone pairs, and hydrogens on nitrogen for structures



Solved The Guanidine Group Is A Common Functional Group I Chegg Com



Protonation Of Guanidine Chemistry Stack Exchange


Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amin Chegg Com


Marine Drugs Free Full Text Guanidine Alkaloids From The Marine Sponge Monanchora Pulchra Show Cytotoxic Properties And Prevent Egf Induced Neoplastic Transformation In Vitro Html


Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amin Chegg Com



The Predicted Stabilities Of Resonance Contributors Mcc Organic Chemistry



Common Mistakes When Drawing Resonance Structures Video Khan Academy



Antimicrobial Drugs Bearing Guanidine Moieties A Review Sciencedirect



Solution Structure Backbone Dynamics And Stability Of A Double Mutant Single Chain Monellin Journal Of Biological Chemistry


Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amin Chegg Com
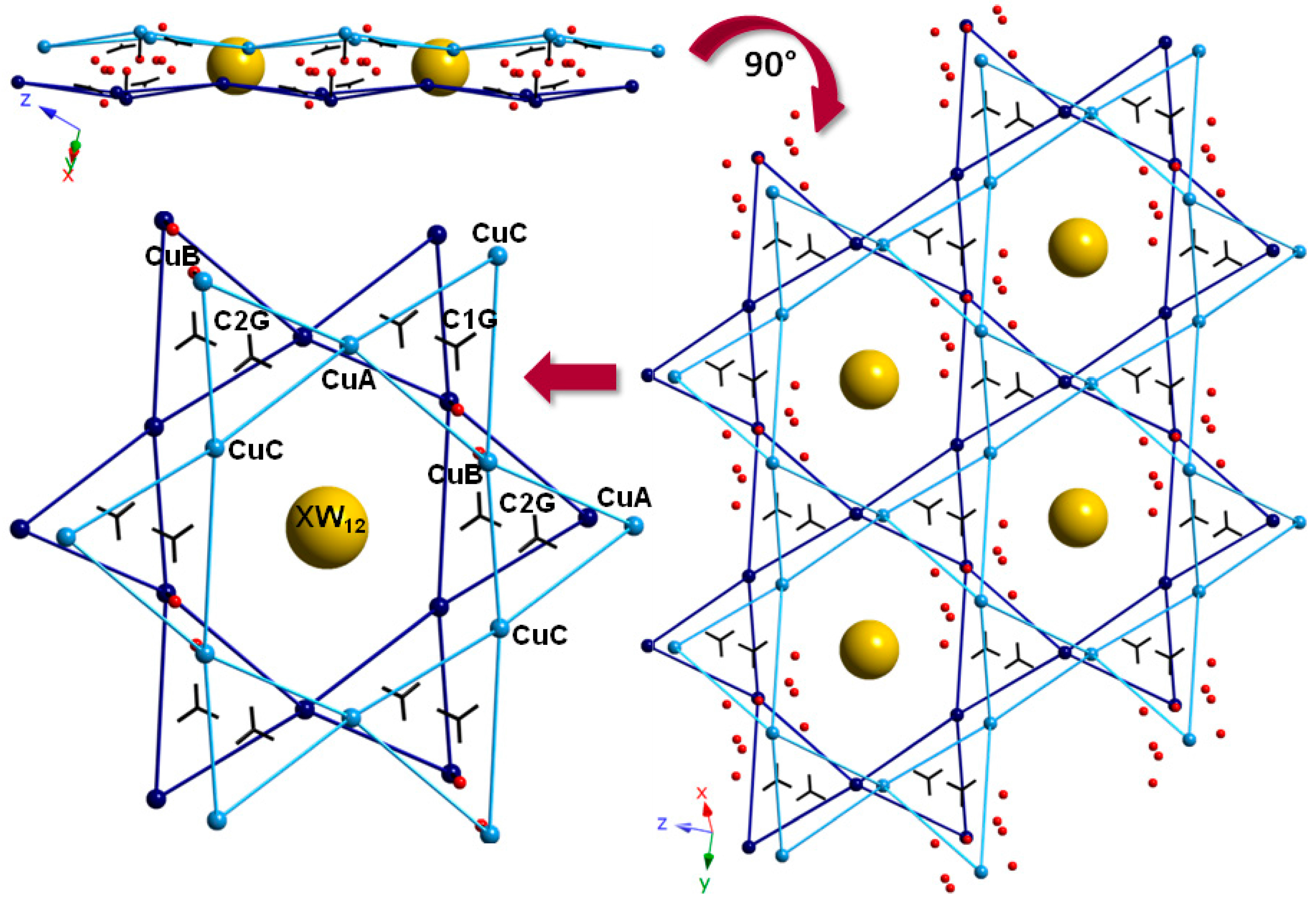


Inorganics Free Full Text Single Crystal To Single Crystal Reversible Transformations Induced By Thermal Dehydration In Keggin Type Polyoxometalates Decorated With Copper Ii Picolinate Complexes The Structure Directing Role Of Guanidinium Html


Mixed Amido Imido Guanidinato Niobium Complexes Synthesis And The Effect Of Ligands On Insertion Reactions Dalton Transactions Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C4dtj


Solved Analyze The Two Compounds Below Circle The Structure Which Is Most Acidic Overall Discuss The Factors That Led You To This Choice Discus Course Hero



Understanding The Guanidine Like Cationic Moiety For Optimal Binding Into The Dna Minor Groove O Sullivan 14 Chemmedchem Wiley Online Library


Solved Analyze The Two Compounds Below Circle The Structure Which Is Most Acidic Overall Discuss The Factors That Led You To This Choice Discus Course Hero



A Facile Route To Metal Nitride Clusterfullerenes By Using Guanidinium Salts A Selective Organic Solid As The Nitrogen Source Yang 10 Chemistry A European Journal Wiley Online Library



Stable 3 Imino 2 3 Dihydroindazol 1 Yl Radicals Quast 11 European Journal Of Organic Chemistry Wiley Online Library


Synthesis Of Guanidines And Some Of Their Biological Applications Springerlink



Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amine The Increased Basicity Can Be Explained By Brainly Com



Major And Minor Resonance Contributing Structures Orgo Basics Vid 7 Youtube


Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amin Chegg Com



Guanidine An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


How To Find The Best Resonance Structure By Applying Electronegativity



Table 1 From Non Covalent Interactions Complexes Of Guanidinium With Dna And Rna Nucleobases Semantic Scholar


5 Key Basicity Trends Of Amines Master Organic Chemistry



Pdf Non Covalent Interactions Complexes Of Guanidinium With Dna And Rna Nucleobases Semantic Scholar



Unusual Oxidative Chemistry Ofn W Hydroxyarginine And N Hydroxyguanidine Catalyzed At An Engineered Cavity In A Heme Peroxidase Journal Of Biological Chemistry


Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amin Chegg Com



Resonance Structure Amine Page 1 Line 17qq Com


Solved Please Help Me Find The Major And Minor Resonance Chegg Com


Solved Which Of The Following Two Structures For Guanidin Chegg Com



Synthesis And Characterization Of A New Energy Material Guanidinium Dinitramide With Crystallization Solvent Sciencedirect



Resonance Structure Amine Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Figure 1 From Non Covalent Interactions Complexes Of Guanidinium With Dna And Rna Nucleobases Semantic Scholar


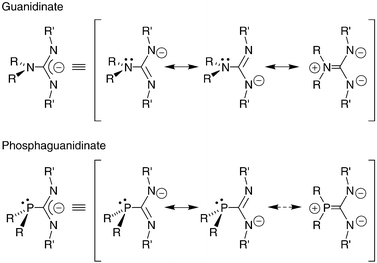
Scheme 1 I Resonance Structures Of Guanidinate Anions Ii Synthetic Download Scientific Diagram



The Rough Energy Landscape Of Superfolder Gfp Is Linked To The Chromophore Abstract Europe Pmc



Circular Dichroism And Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Analysis Of Immunogenic Gluten Peptides And Their Analogs Journal Of Biological Chemistry


Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amin Chegg Com



Protein Stiffening And Entropic Stabilization In The Subdenaturing Limit Of Guanidine Hydrochloride Biophysical Journal



The Rough Energy Landscape Of Superfolder Gfp Is Linked To The Chromophore Abstract Europe Pmc



Why There Is A Huge Difference Between The Basicity Of Urea And Guanidine Chemistry Stack Exchange



Solved Draw Resonance Structures And Arrow Pushing Indic Chegg Com


Lithium And Aluminium Complexes Supported By Chelating Phosphaguanidinates Dalton Transactions Rsc Publishing
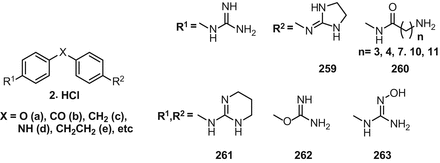


Synthesis Of Guanidines And Some Of Their Biological Applications Springerlink



An Approach To Bioactivity Assessment For Critical Quality Attribute Identification Based On Antibody Antigen Complex Structure Journal Of Pharmaceutical Sciences



5 Methylcyclopentadiene Undergoes Homolytic Bond Cleavage Of A C H Bond To Form A Radical That Brainly Com



Answer Use Line Angle Skeletal Structur Clutch Prep



The Binding Of Modified Analogs Of Guanidine Bound To The G Violaceus Download Scientific Diagram


Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amin Chegg Com


Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amin Chegg Com


Pdf The Structure Of The Guanidine Ii Riboswitch



Of Two Possible Structures A And B For The Clutch Prep



Urea But Not Guanidinium Destabilizes Proteins By Forming Hydrogen Bonds To The Peptide Group Pnas



Major And Minor Resonance Contributing Structures Orgo Basics Vid 7 Youtube



A Proton Transfer Reaction Can Occur When An Aldehyde Is Placed In Strong Base Such As An Alkoxide Brainly Com



Of Two Possible Structures A And B For The Clutch Prep



Structure Of Guanidine Tbd 4 Left Its Corresponding Guanidinium Download Scientific Diagram
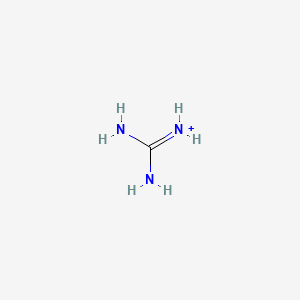


Guanidinium Ch6n3 Pubchem


Chemical Forums Resonance And Basicity


Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amin Chegg Com


Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amin Chegg Com



With Aid Of Resonance Structures Show That Proton Transfer To Guanidine Occurs Preferentially To Its Nh B Than Its Nh 2 A Groups Study Com



Major And Minor Resonance Contributing Structures Orgo Basics Vid 7 Youtube



Stable 3 Imino 2 3 Dihydroindazol 1 Yl Radicals Quast 11 European Journal Of Organic Chemistry Wiley Online Library


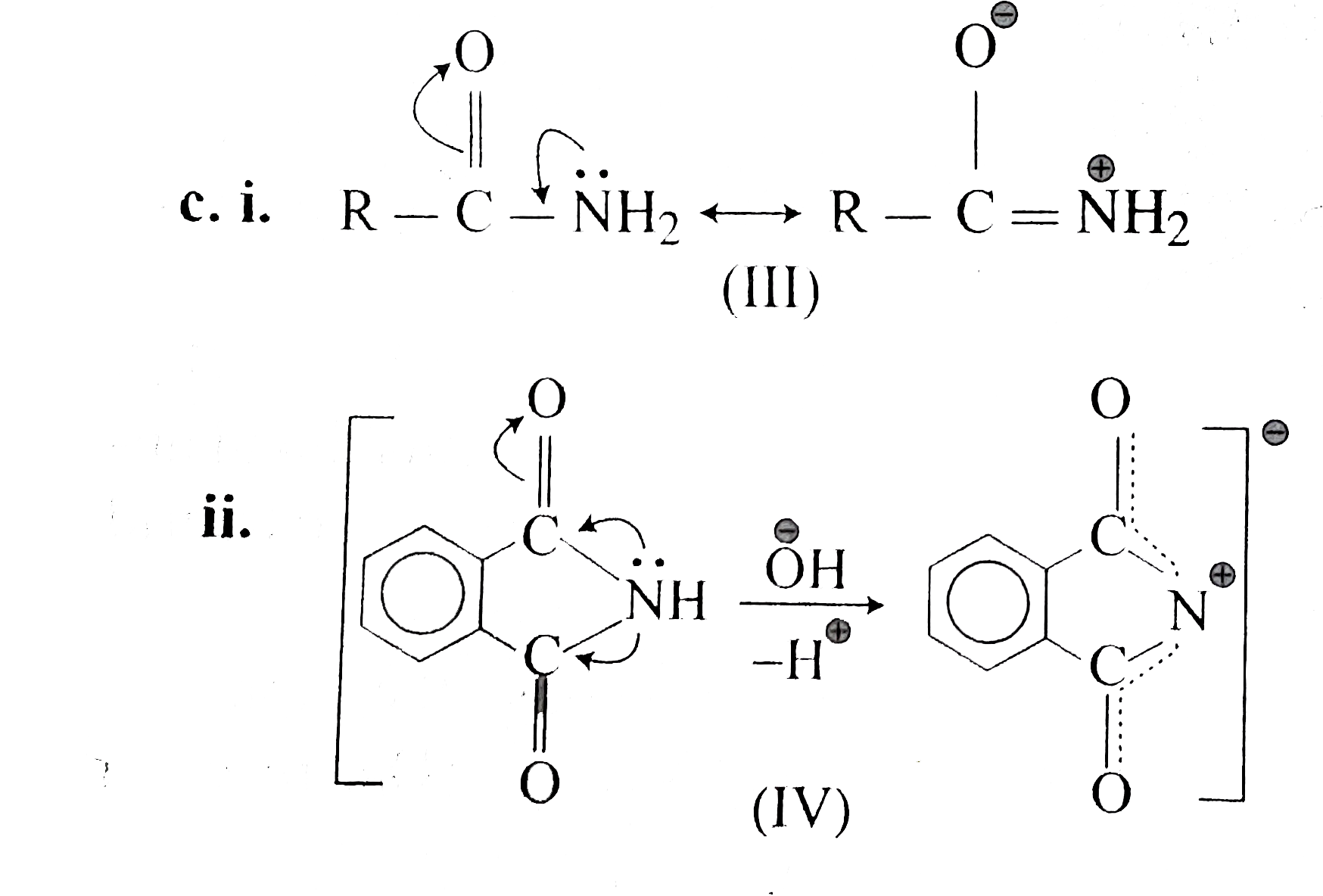
Exam 3 Answer Key


Major And Minor Resonance Structures Organic Chemistry Socratic



Resonance Structures Of Amide Uracil Derivatives And Their Download Scientific Diagram



Guanidine An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Structural Basis For Ligand Binding To The Guanidine I Riboswitch Sciencedirect



Answer Use Line Angle Skeletal Structur Clutch Prep



No comments:
Post a Comment